10 maps to understand Gaza's tumultuous history
NewsFrom Egyptian occupation to Hamas control, this enclave, which has now been sealed off by Israel, is at the heart of the Middle East conflict.
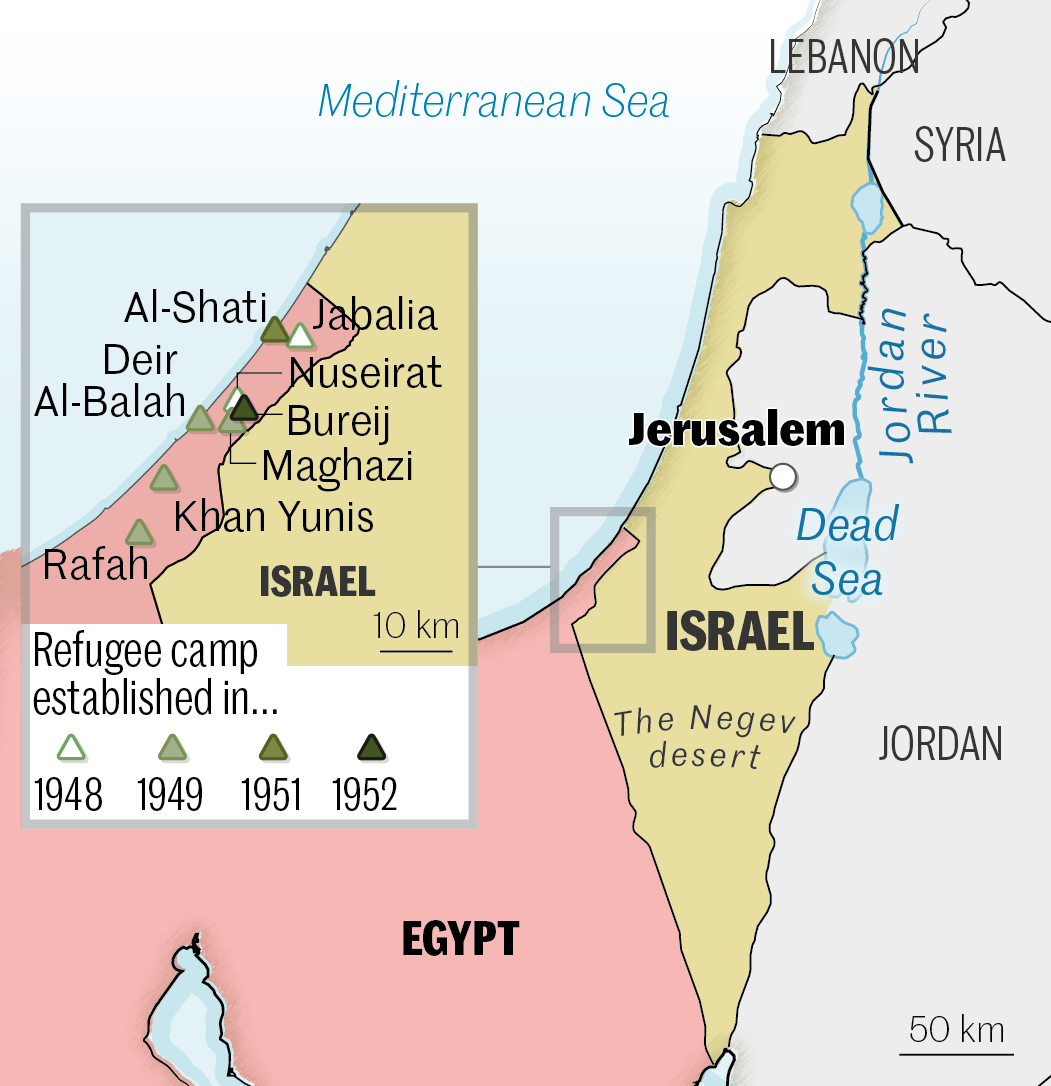
1948. Creation of the State of Israel
Israel came into being on May 14, 1948, as a result of the United Nations' partition plan, which divided British Mandate Palestine into two states, one Jewish and the other Arab. The next day, the neighboring Arab countries declared war on Israel, which ended in an Israeli victory on March 10, 1949.
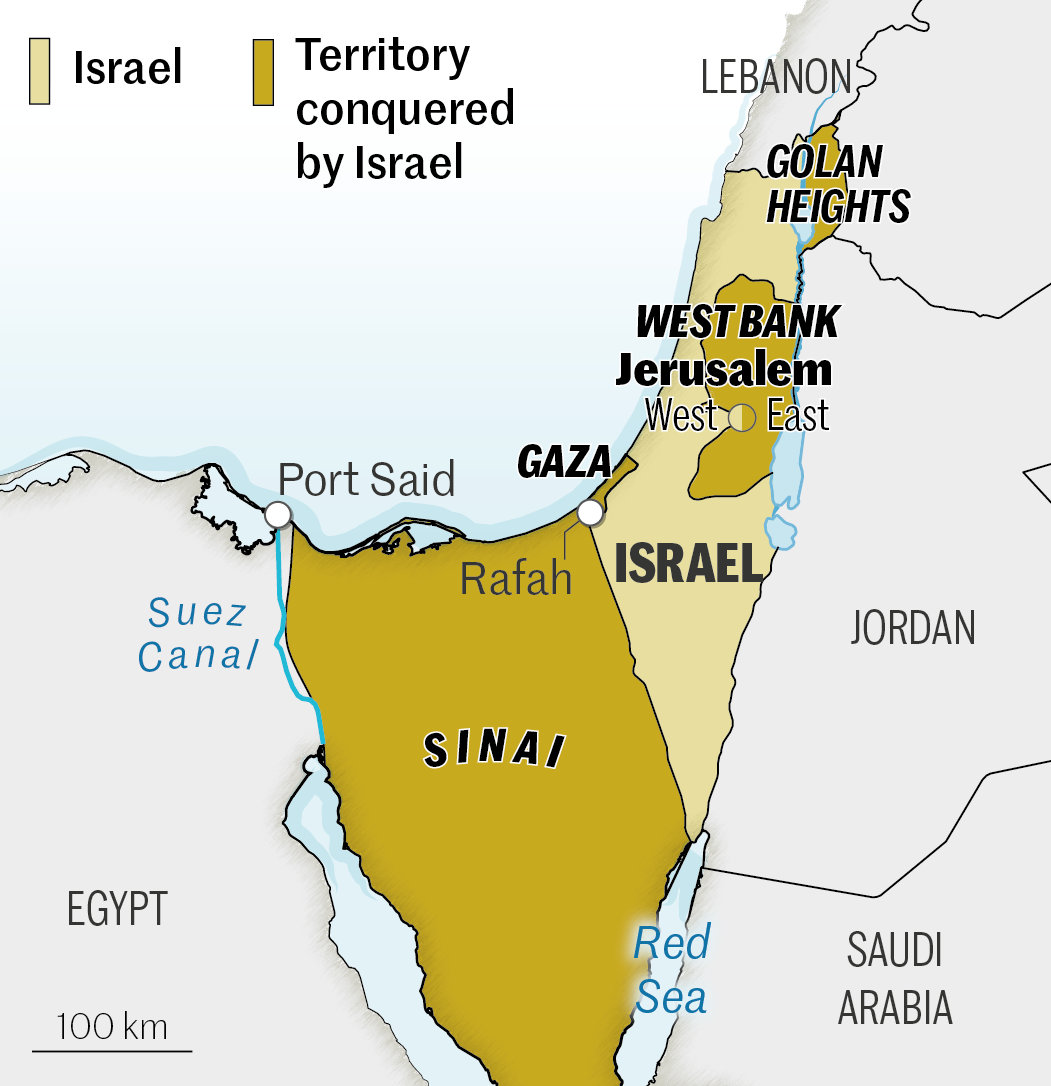
1956. Suez Crisis
After Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal, Israel invaded the Gaza Strip and Sinai with French and British support. Under pressure from the USSR and the USA, Israel retreated behind the 1949 armistice line. The UN deployed peacekeepers along the Egyptian border.
1979. Egypt–Israel peace treaty
Israel returns Sinai to Egypt (1982), but retains control of Gaza.
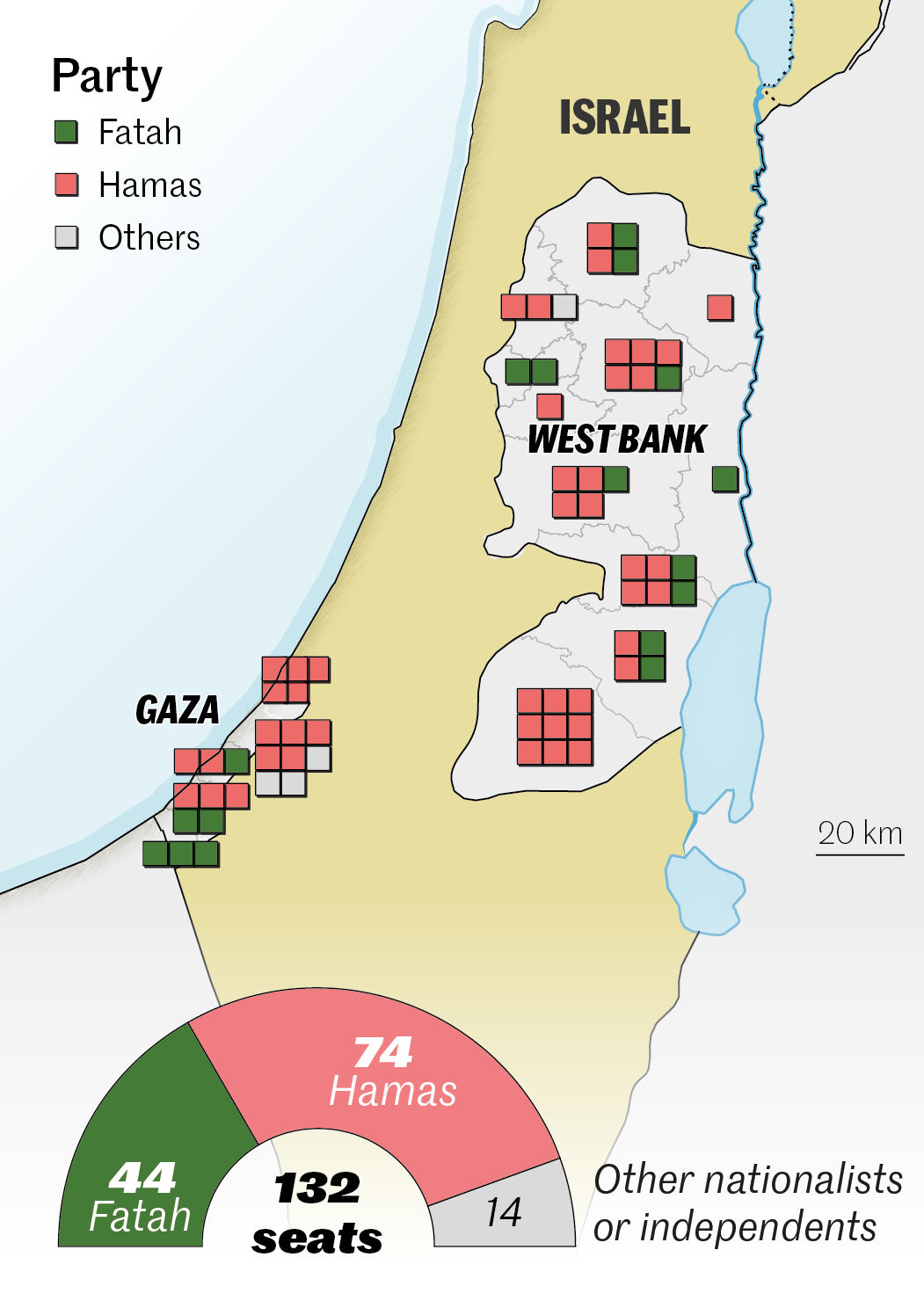
1987. First Intifada and creation of Hamas
Starting in Gaza on December 9, 1987, the first Intifada set the Palestinian territories ablaze. The Islamic Resistance Movement (Hamas), an offshoot of the Muslim Brotherhood, was created. Its charter (1988) advocates for the destruction of Israel.
2000. Second Intifada
On September 28, Israeli right-wing leader Ariel Sharon's visit to the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound triggered a new Palestinian uprising. Israel bombed Gaza and destroyed the international airport. A wave of suicide bombings hit Israel. Sheikh Ahmed Yassin, founder and spiritual leader of Hamas, is killed in an Israeli strike in Gaza on March 22, 2004.
2006. Operation Summer Rains
Between June 28 and November 26, Israel launched a military operation in Gaza to free Corporal Gilad Shalit, kidnapped by a Palestinian squad, and to weaken Hamas's arsenal. He was released in 2011, in exchange for the release of 1,027 Palestinians detained in Israel, including Yahya Sinwar, the current head of Hamas in Gaza since 2017.
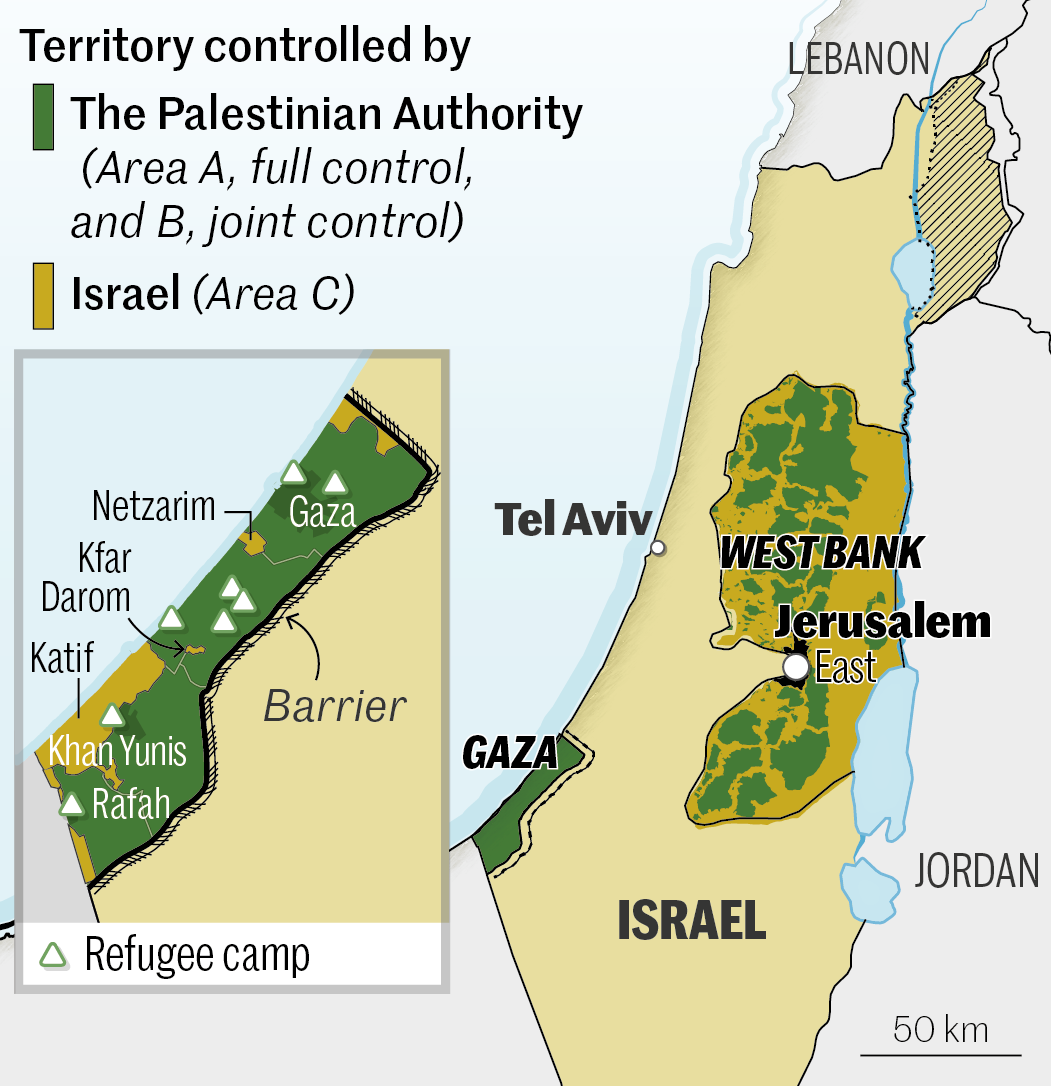
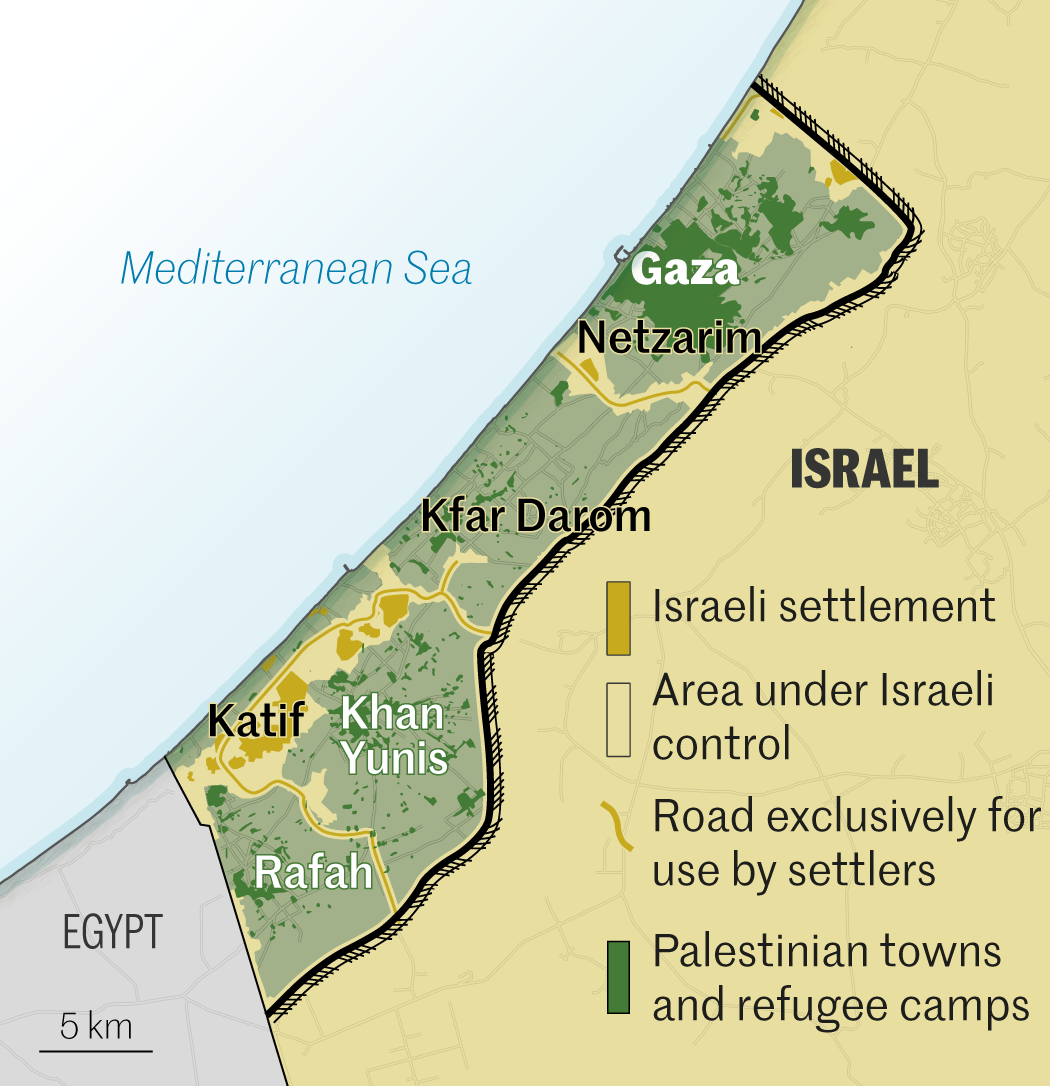
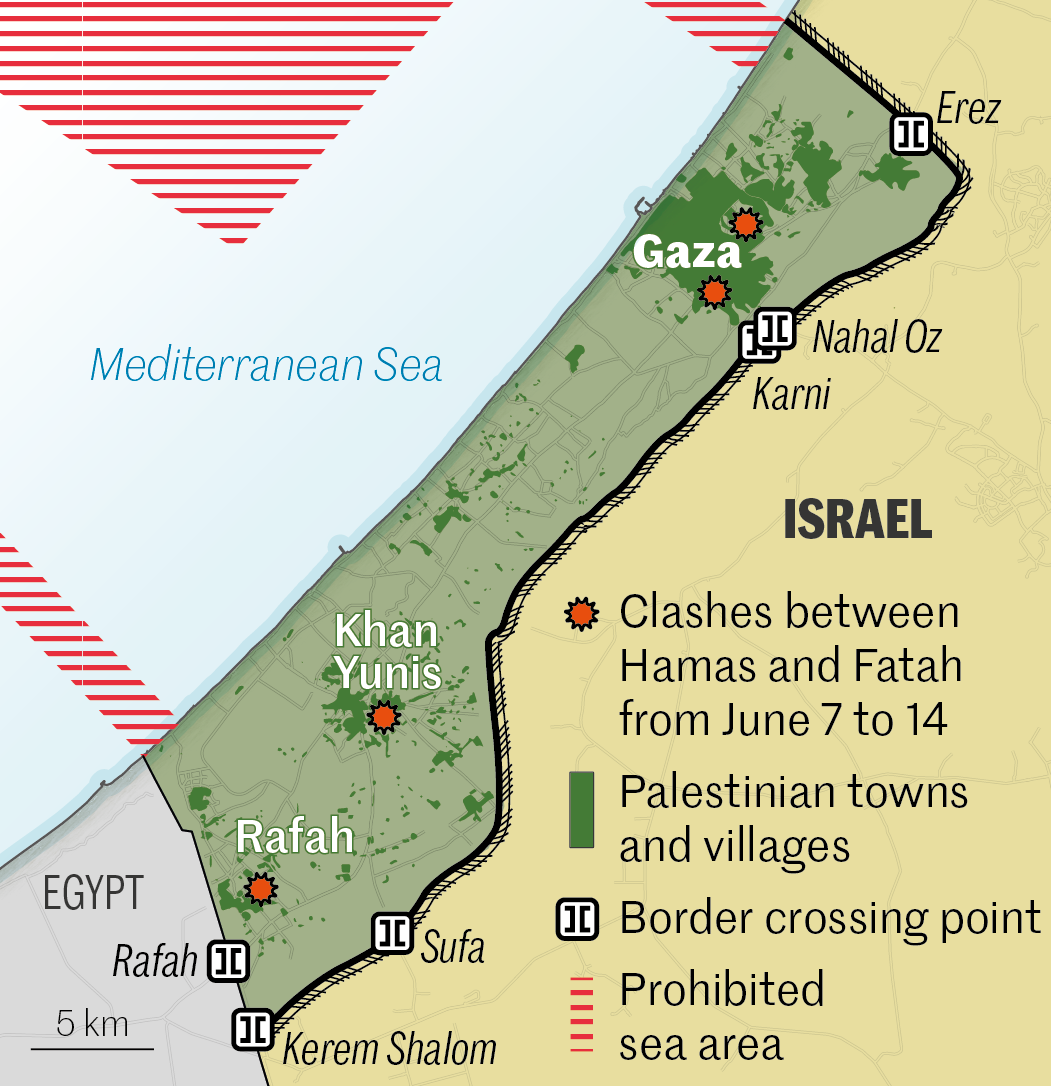
2007. Israeli-Egyptian blockade
With Hamas in power, the Gaza Strip was declared a "hostile entity" by Israel, which set up a blockade. Land crossings into Israel were closed or severely restricted. Access to the sea was restricted. Egypt also closed its border with Gaza, and erected a wall. These hardships left the population destitute, but did not weaken Hamas.
Late 2008. Operation Cast Lead
Israel launched an air and ground offensive to destroy Hamas facilities and tunnels under the border with Egypt.
2011: Iron Dome
Deployment of the Israeli air defense system to intercept rockets launched from southern Lebanon and Gaza.
2012. Operation Pillar of Defense
On November 14, the Israeli army launched an offensive in Gaza. It began with the elimination of Ahmed Jabari, a leader of the military wing of Hamas, and ended a week later with massive air strikes.
You have 27.15% of this article left to read. The rest is for subscribers only.