
Each year, Gallup conducts a survey of American adults on various economic topics, including the country’s central bank, the Federal Reserve.
More specifically, respondents are asked how much confidence they have in the current Fed chairman to do or recommend the right thing for the U.S. economy.
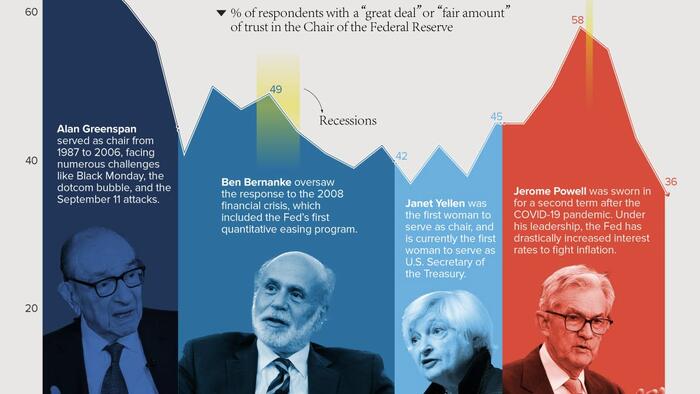
Visual Capitalist's Marcus Lu and Bhabna Banerjee visualized these results from 2001 to 2023 to see how confidence levels have changed over time.
The data used in this infographic is also listed in the table below. Percentages reflect the share of respondents that have either a “great deal” or “fair amount” of confidence.
Data for 2023 collected April 3-25, with this statement put to respondents: “Please tell me how much confidence you have [in the Fed chair] to recommend the right thing for the economy.”
We can see that trust in the Federal Reserve has fluctuated significantly in recent years.
For example, under Alan Greenspan, trust was initially high due to the relative stability of the economy. The burst of the dotcom bubble—which some attribute to Greenspan’s easy credit policies—resulted in a sharp decline.
On the flip side, public confidence spiked during the COVID-19 pandemic. This was likely due to Jerome Powell’s decisive actions to provide support to the U.S. economy throughout the crisis.
Measures implemented by the Fed include bringing interest rates to near zero, quantitative easing (buying government bonds with newly-printed money), and emergency lending programs to businesses.
After peaking at 58%, those with a “great deal” or “fair amount” of trust in the Fed chair have tumbled to 36%, the lowest number in 20 years.
This is likely due to Powell’s hard stance on fighting post-pandemic inflation, which has involved raising interest rates at an incredible speed. While these rate hikes may be necessary, they also have many adverse effects:
Higher rates have also prompted many U.S. tech companies to shrink their workforces, and have been a factor in the regional banking crisis, including the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank.
