Authored by Mike Shedlock via MishTalk.com,
Let's discuss the warnings of PJM Interconnect, the operator of the nation's largest competitive market for electricity.
Before reviewing the PJM Interconnect February 2023 report, let's take a look at policies and regulations.
Next, consider the Inside Climate News report The Largest U.S. Grid Operator Puts 1,200 Mostly Solar Projects on Hold for Two Years
The nation’s largest electrical grid operator has approved a new process for adding power plants to the sprawling transmission system it manages, including a two-year pause on reviewing and potentially approving some 1,200 projects, mostly solar power, that are part of a controversial backlog.
Over the last four years, PJM officials have said they have experienced a fundamental shift in the number and type of energy projects seeking to be added to a grid, each needing careful study to ensure reliability. It used to be that PJM would see fewer, but larger, fossil fuel proposals. Now, they are seeing a larger number of smaller, largely renewable energy projects.
A new approval process will put projects that are the readiest for construction at the front of the line, and discourage those that might be more speculative or that have not secured all their financing.
Then, an interim period will put a two-year delay on about 1,250 projects in their queue—close to half of the total—and defer the review of new projects until the fourth quarter of 2025, with final decisions on those coming as late as the end of 2027.
Now let's now take a look at Energy Transition in PJM: Resource Retirements, Replacements & Risks released February 24, 2023.
Our research highlights four trends below that we believe, in combination, present increasing reliability risks during the transition, due to a potential timing mismatch between resource retirements, load growth and the pace of new generation entry under a possible “low new entry” scenario:
The growth rate of electricity demand is likely to continue to increase from electrification coupled with the proliferation of high-demand data centers in the region. Retirements are at risk of outpacing the construction of new resources, due to a combination of industry forces, including siting and supply chain, whose long-term impacts are not fully known. PJM’s interconnection queue is composed primarily of intermittent and limited-duration resources. Given the operating characteristics of these resources, we need multiple megawatts of these resources to replace 1 MW of thermal generation.
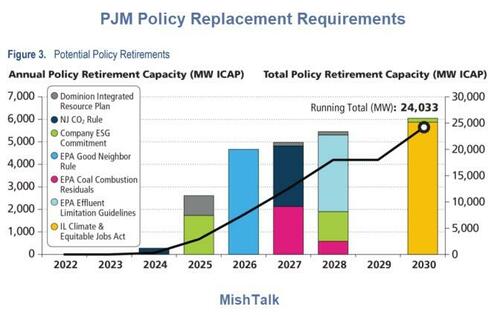
The analysis shows that 40 GW of existing generation are at risk of retirement by 2030. This figure is composed of: 6 GW of 2022 deactivations, 6 GW of announced retirements, 25 GW of potential policy-driven retirements and 3 GW of potential economic retirements. Combined, this represents 21% of PJM’s current installed capacity.
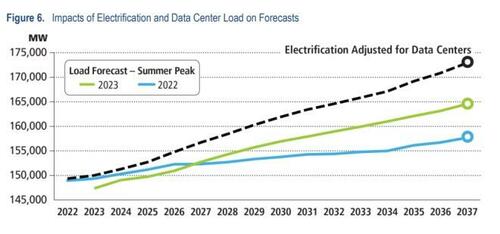
In addition to the retirements, PJM’s long-term load forecast shows demand growth of 1.4% per year for the PJM footprint over the next 10 years. Due to the expansion of highly concentrated clusters of data centers, combined with overall electrification, certain individual zones exhibit more significant demand growth – as high as 7% annually.
For the first time in recent history, PJM could face decreasing reserve margins should these trends continue. The amount of generation retirements appears to be more certain than the timely arrival of replacement generation resources and demand response, given that the quantity of retirements is codified in various policy objectives, while the impacts to the pace of new entry of the Inflation Reduction Act, post-pandemic supply chain issues, and other externalities are still not fully understood.
Recent movement in the natural gas spot markets across the U.S. and Europe add another degree of uncertainty to future operations. In 2022, European natural gas supply faced many challenges resulting from the war in Ukraine and subsequent sanctions against Russia. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) imports into the EU and the U.K. in the first half of 2022 increased 66% over the 2021 annual average, primarily from U.S. exporters with operational flexibility. This international natural gas demand is a new competitor for domestic spot-market consumers, resulting in significantly higher fuel costs for PJM’s natural gas fleet.
Along with the energy transition, PJM is witnessing a large growth in data center activity. Importantly, the PJM footprint is home to Data Center Alley in Loudoun County, Virginia, the largest concentration of data centers in the world. PJM uses the Load Analysis Subcommittee (LAS) to perform technical analysis to coordinate information related to the forecast of electrical peak demand. In 2022, the LAS began a review of data center load growth and identified growth rates over 300% in some instances.
Additionally, PJM is expecting an increase in electrification resulting from state and federal policies and regulations. The study therefore incorporates an electrification scenario in the load forecast to provide insight on capacity need should accelerated electrification drive demand increases.
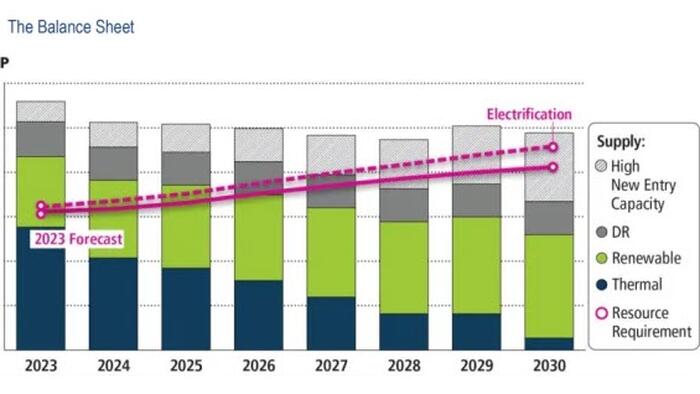
Combining the resource exit, entry and increases in demand, summarized in Figure 7, the study identified some areas of concern. Approximately 40 GW PJM’s fossil fuel fleet resources may be pressured to retire as load grows into the 2026/2027 Delivery Year.
The projected total capacity from generating resources would not meet projected peak loads, thus requiring the deployment of demand response. By the 2028/2029 Delivery Year and beyond, at Low New Entry scenario levels, projected reserve margins would be 8%, as projected demand response may be insufficient to cover peak demand expectations, unless new entry progresses at a levels exhibited in the High New Entry scenario. This will require the ability to maintain needed existing resources, as well as quickly incentivize and integrate new entry
The 2024/2025 BRA, which executed in December 2022, highlighted another area of uncertainty. Queue capacity with approved ISAs/WMPAs is currently very high, approximately 35 GW-nameplate, but resources are not progressing into construction.
There has only been about 10 GW-nameplate moving to in service in the past three years. There may still be risks to new entry, such as semiconductor supply chain disruptions or pipeline supply restrictions, which are preventing construction despite resources successfully navigating the queue process.
After applying the logistical regression model for 10 years of historical project completion (Y-queue to present) without project stage, approximately 15.3 GW-nameplate/8.7 GW-capacity were deemed commercially probable out of 178 GW of projects examined.
The model results for thermal resources were reasonably in line with expectations. However, the model produced extremely low entry from onshore wind, offshore wind, solar, solar-hybrid and storage resources.
In case you missed it, please consider Question of the Day - How Fast Will the Shift to EVs happen?
The faster the shift, the higher and faster the inflation.
* * *