
Across the United States, median full-time salaries vary widely depending on the state. From booming coastal economies to regions with lower costs of living, geographic differences play a major role in shaping income levels.
This visualization, via Visual Capitalist's Niccolo Conte, maps out the median full-time salary by state in 2024 using data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey, the latest data available as of September 2025.
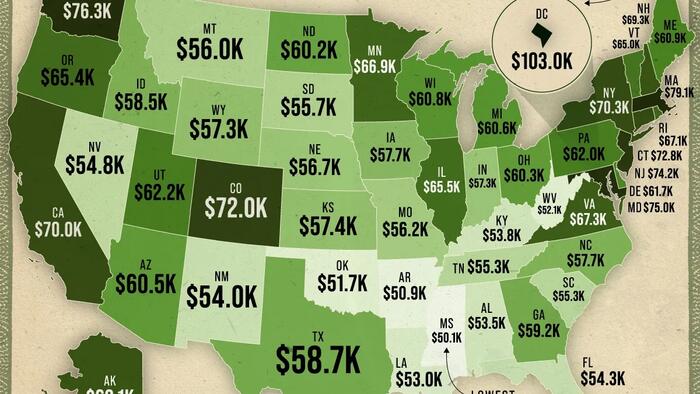
The U.S. overall median full-time salary sits at approximately $61,702 per year, though the gap between the highest and lowest earning states exceeds $50,000.
The data table below shows the median earnings of the full-time, year-round civilian workforce aged 16 and older in every U.S. state:
At the very top is the District of Columbia, where the median full-time salary reaches $102,970—well above any state.
Massachusetts ($79,113), Washington ($76,323), Maryland ($74,982), and New Jersey ($74,164) round out the top five. These states benefit from strong tech, finance, and government sectors that boost wages significantly above the national level.
While it’s primarily coastal states that have a median full-time salary above $70,000, Colorado is the notable exception of a landlocked state with higher median earnings at $72,028.
At the other end of the spectrum, Mississippi ranks last with a median full-time salary of $50,120.
Other low-earning states include Arkansas ($50,899), Oklahoma ($51,676), West Virginia ($52,080), and Louisiana ($52,959). Many of these states are concentrated in the South, reflecting broader regional wage gaps tied to industry mix, job availability, and cost of living.
A clear divide emerges between coastal and interior states. High salaries cluster in the Northeast and on the West Coast, while much of the South lags behind the U.S. median of $61,702.
To learn more about earnings in the U.S., check out this graphic which breaks down how education affects earnings in every single state on Voronoi, the new app from Visual Capitalist.
