STOCKHOLM, Sweden (AP) — A US-Japanese trio on Monday won the Nobel Prize in Medicine for research into how the immune system is kept in check by identifying its “security guards,” the Nobel jury said.
The discoveries by Mary E. Brunkow and Fred Ramsdell of the United States and Japan’s Shimon Sakaguchi have been decisive for understanding how the immune system functions and why we do not all develop serious autoimmune diseases.
Sakaguchi, a professor at the Immunology Frontier Research Centre in Osaka, told Swedish broadcaster Sveriges Radio: “It’s an honor for me. I’m looking forward to visiting Stockholm in December” to receive the award in person.
The Nobel committee was however unable to reach the two US-based laureates to break the news to them in person.
“If you hear this, call me,” the head of the Nobel Assembly, Thomas Perlmann, joked at the press conference announcing the winners.
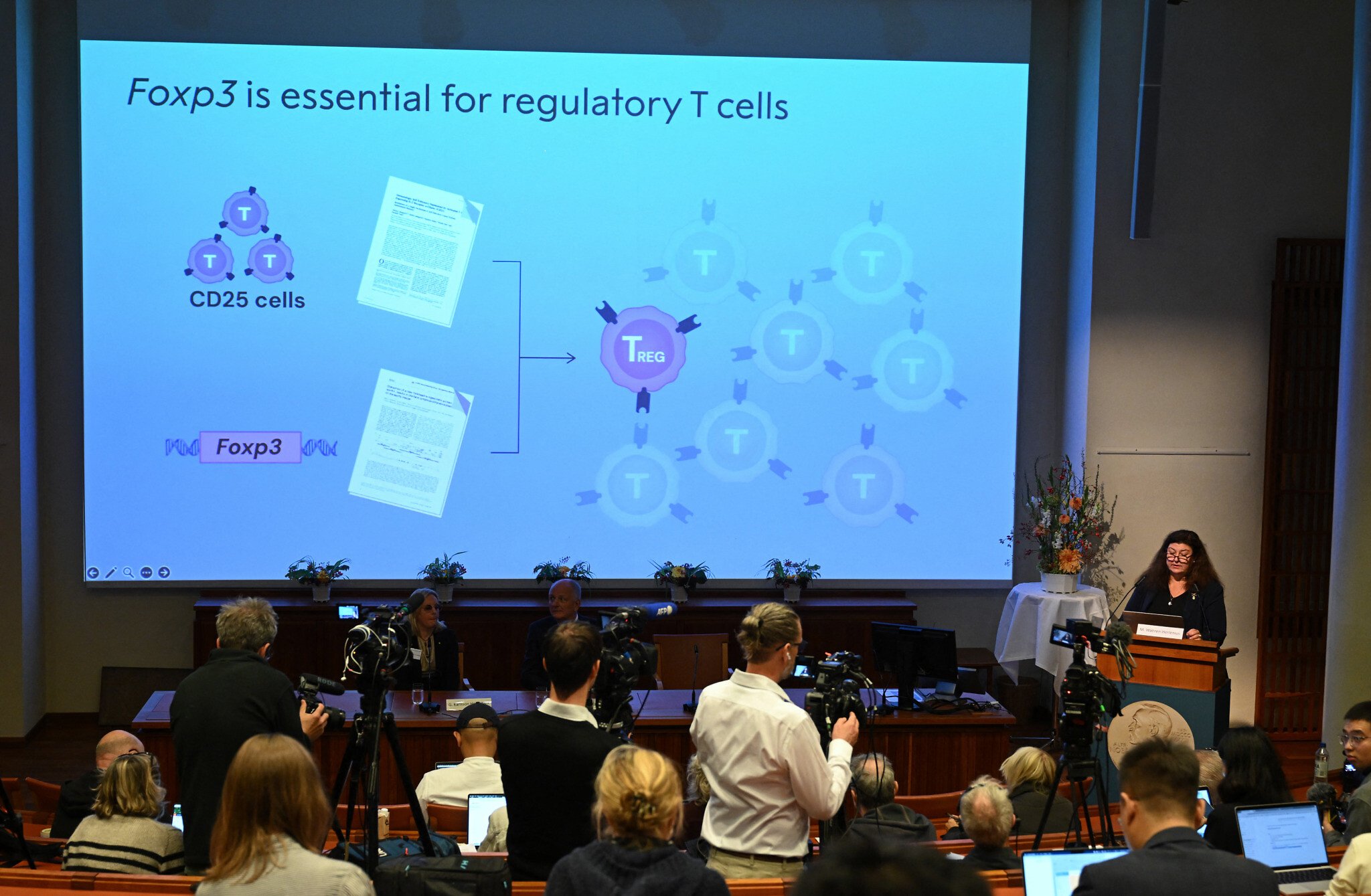
The three won the prize for research that identified the immune system’s “security guards,” called regulatory T-cells.
Their work concerns “peripheral immune tolerance” that prevents the immune system from harming the body, and has led to a new field of research and the development of potential medical treatments now being evaluated in clinical trials.
“The hope is to be able to treat or cure autoimmune diseases, provide more effective cancer treatments and prevent serious complications after stem cell transplants,” the jury said.
Sakaguchi made the first key discovery in 1995.
At the time, many researchers were convinced that immune tolerance only developed due to potentially harmful immune cells being eliminated in the thymus, through a process called “central tolerance.”
Sakaguchi, 74, showed that the immune system is more complex and discovered a previously unknown class of immune cells, which protect the body from autoimmune diseases.
Brunkow, born in 1961 and a senior project manager at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle, and Ramsdell, a 64-year-old senior advisor at Sonoma Biotherapeutics in San Francisco, made the other key discovery in 2001, when they were able to explain why certain mice were particularly vulnerable to autoimmune diseases.
“They had discovered that mice have a mutation in a gene that they named Foxp3,” the jury said.
“They also showed that mutations in the human equivalent of this gene cause a serious autoimmune disease, IPEX.”
Two years later, Sakaguchi was able to link these discoveries.
The trio will receive their prize — a diploma, a gold medal and $1.2 million split three ways — at a formal ceremony in Stockholm on December 10.
Researchers from major US institutions typically dominate the Nobel science prizes, due largely to the US’s longstanding investment in basic science and academic freedoms.
But that could change down the line following massive US budget cuts to science programs announced by President Donald Trump.
Since January, the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) has terminated 2,100 research grants totaling around $9.5 billion and $2.6 billion in contracts, according to an independent database called Grant Watch.