
“Low back pain” which can be acute or chronic, is literally pain or discomfort of the lower lumbar region of the back. Acute back pain usually follows some kind of injury, often related to everyday activities such as housework, gardening, a sports-related injury, or an automobile accident. Back pain that lasts for more than three months is classified as chronic.
Symptoms are often described as muscle aches but can include shooting or stabbing pain, limited flexibility and range of motion, or an inability to stand straight.
Most cases of low back pain are due to strain on the bones, muscles, and ligaments of the spine. In some cases, however, low back pain can be due to such serious conditions as cancer or structural problems of the spine, which can cause nerve damage.
Occasionally, lower back pain is due to a “slipped disk” (also called a herniated disk), in which one of the disks of cartilage that separates the vertebrae in the spine bulges out of place and presses on nerves. Often, a disk “slips” as a result of twisting while lifting, but the cause may not be identifiable.
Simple preventive steps can help eliminate recurring back pain resulting from improper body mechanics or from other causes of back problems that don’t stem from injuries. Exercises that tone the back and maintaining proper posture are especially helpful. In addition, anyone with a tendency to develop back pain should learn to lift objects properly:
Choosing ergonomic furniture and tools at home and at work can also help avoid strains on the back.
Most acute back pain will resolve on its own within two weeks without medical intervention. Whether lower back pain is acute or chronic, most cases are initially treated with over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce discomfort and with anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce inflammation. Sometimes, prescription drugs may be recommended for pain relief and to allow quality sleep.
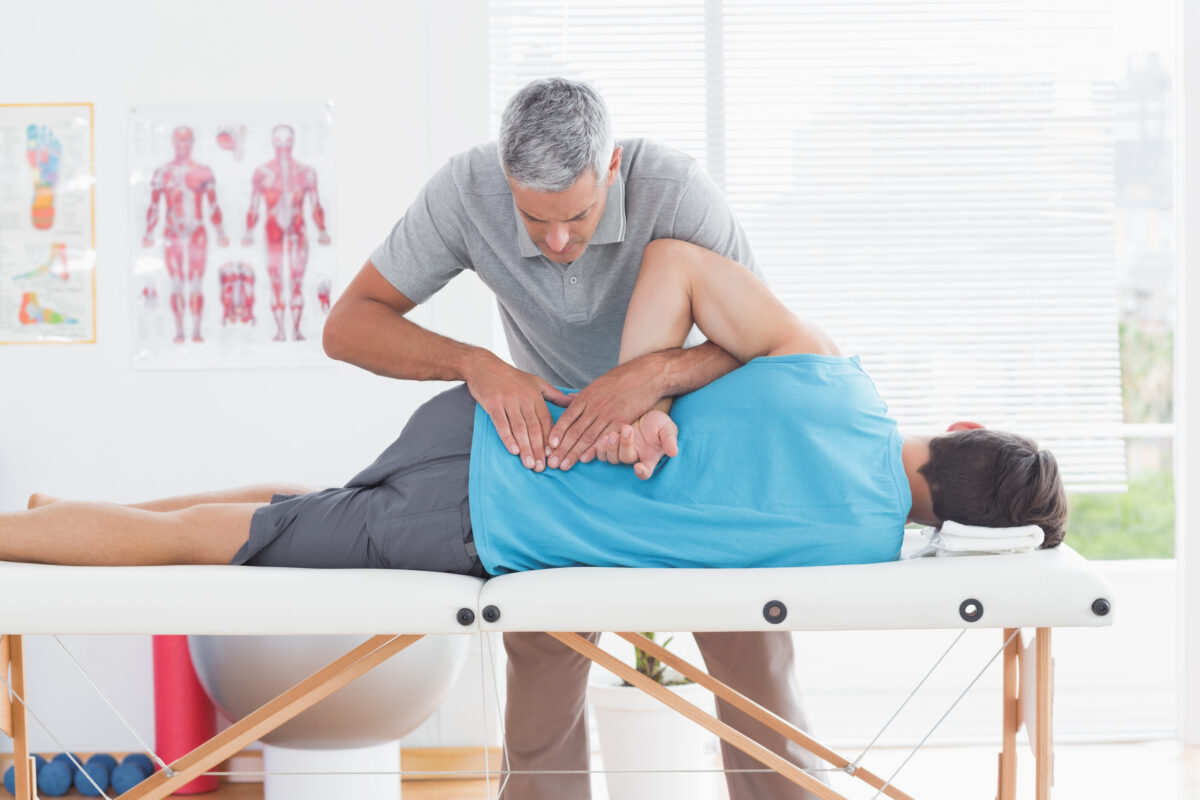
Cold and hot compresses may help reduce pain and inflammation and allow greater mobility, although they have not been scientifically proven to quickly resolve low back injury. Bed rest is recommended for only one to two days at most, and patients are advised to resume their normal activities as soon as possible. Massage therapy can be very useful in cases of acute muscle spasm causing back pain and problems with flexibility.
Exercise may be the best way to speed recovery and strengthen back and abdominal muscles. Physical therapy may be recommended for more severe strains. In the most serious cases that don’t respond to other forms of treatment, and that involve compromised structures in the spine, surgery may be recommended to relieve pain caused by back problems or serious musculoskeletal injuries.
Read one or both books on back pain by Dr. John Sarno, a physician and professor of rehabilitation medicine at New York University. Sarno believes that most chronic back pain stems from a condition he calls tension myositis syndrome (TMS). Myositis means muscle inflammation. According to Sarno, TMS is a combination of muscle spasm and inflammation stemming from an unbalanced pattern of nerve signaling to nearby muscles and interference with their blood supply.
Sarno explains his theory in his books “Healing Back Pain: The Mind-Body Connection” (Warner Books, 1991) and “Mindbody Prescription: Healing the Body, Healing the Pain” (Warner Books, 1998). The treatment he recommends is aimed at changing patterns of thinking, feeling, and handling stress, all of which have contributed to the pain. You also can try the following approaches:
In addition, perform strength training exercises at least twice a week to tone and firm the abdominal, leg, and buttock muscles that help to support the back. Seek out proper instruction before embarking on a strength training program—using either free weights or weight machines improperly can defeat the purpose. Make sure you do some stretching or yoga for flexibility.
Republished from DrWeil.com
