The Institute for the Study of War reported 8 August that surrendering remaining territories in Donetsk Oblast as a ceasefire prerequisite without securing a final peace agreement would grant Russian forces tactical advantages for future military operations.
“The surrender of the rest of Donetsk Oblast as the prerequisite of a ceasefire with no commitment to a final peace settlement ending the war would position Russian forces extremely well to renew their attacks on much more favorable terms, having avoided a long and bloody struggle for the ground,” the ISW analysed.
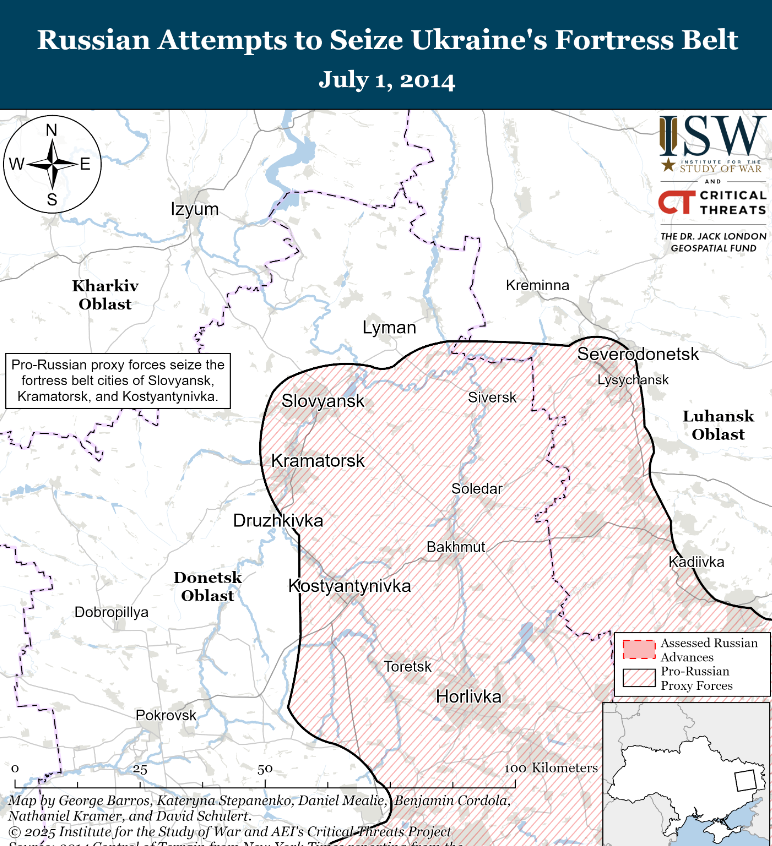
Such concessions would compel Ukraine to abandon what the institute terms its “fortress belt” — the primary fortified defensive line established in Donetsk Oblast in 2014. The ISW emphasizes that “conceding such a demand would force Ukraine to abandon its ‘fortress belt,’ the main fortified defensive line in Donetsk Oblast since 2014 — with no guarantee that fighting will not resume.”
The fortress belt consists of four major cities and multiple smaller settlements positioned along the H-20 Kostyantynivka-Sloviansk highway. The defensive line stretches 50 kilometers from north to south — approximately the distance between Washington, D.C. and Baltimore, Maryland — and housed over 380,537 residents before the current war.
Sloviansk and Kramatorsk anchor the northern section of this defensive network, functioning as logistics hubs for Ukrainian military operations throughout Donetsk Oblast. Kramatorsk currently serves as the oblast’s provisional administrative center, replacing Donetsk City, which remains under Russian occupation. The southern portion of the fortress belt includes Druzhkivka, Oleksiyevo-Druzhkivka, and Kostyantynivka.
The defensive infrastructure originated following Ukraine’s 2014 military operations against pro-Russian proxy forces. These forces initially captured Sloviansk, Kramatorsk, Druzhkivka, and Kostyantynivka in April 2014, but Ukrainian troops regained control by July of that year.
The ISW reports that Ukraine has invested 11 years in strengthening these positions, building “significant defense industrial and defensive infrastructure in and around these cities.” This sustained development effort represents substantial financial and strategic commitments that would be lost under any territorial concession scenario.
The analysis suggests that Russian forces would gain considerable operational advantages by securing these positions without conducting costly urban warfare operations. The fortress belt has served as what the ISW describes as “a major obstacle to the Kremlin’s territorial ambitions in Ukraine over the last 11 years.”